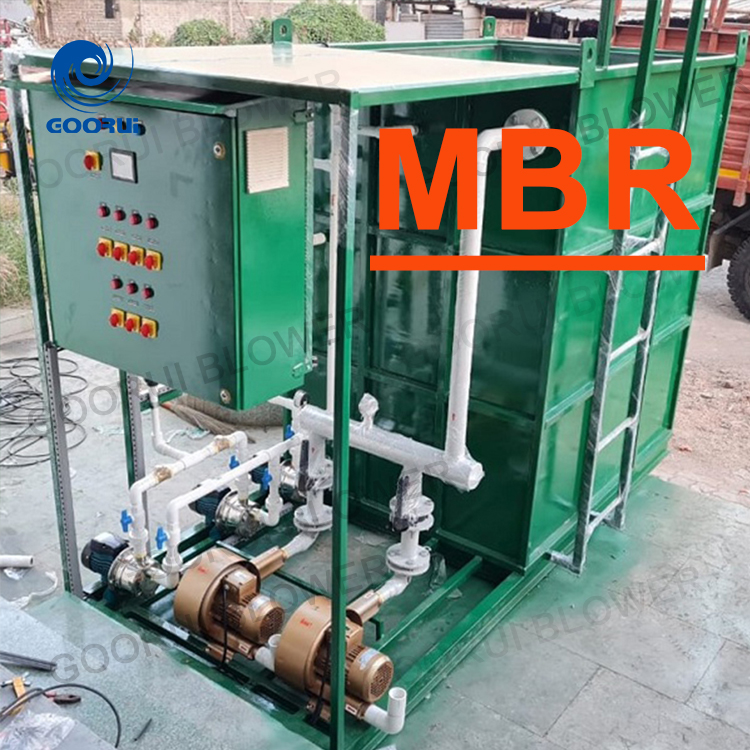
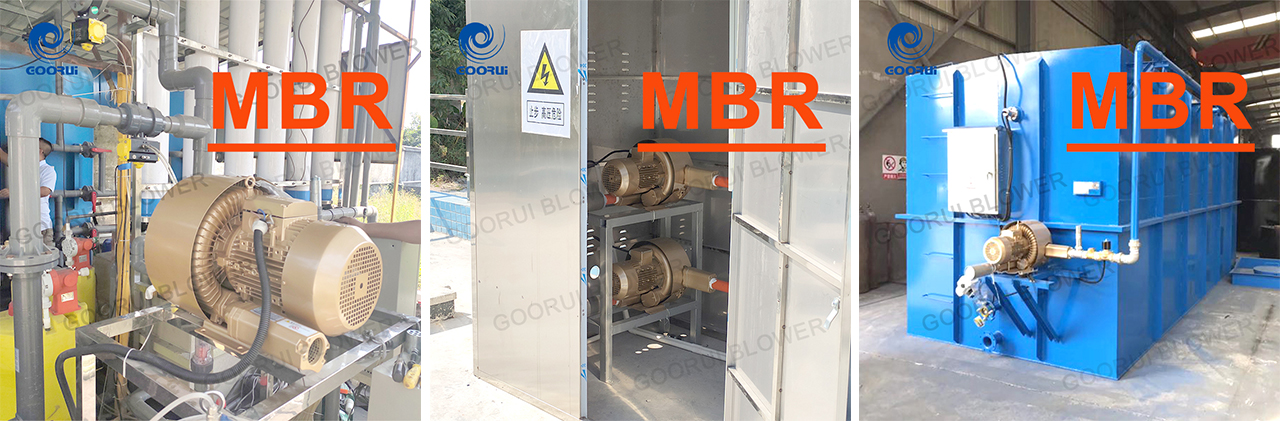
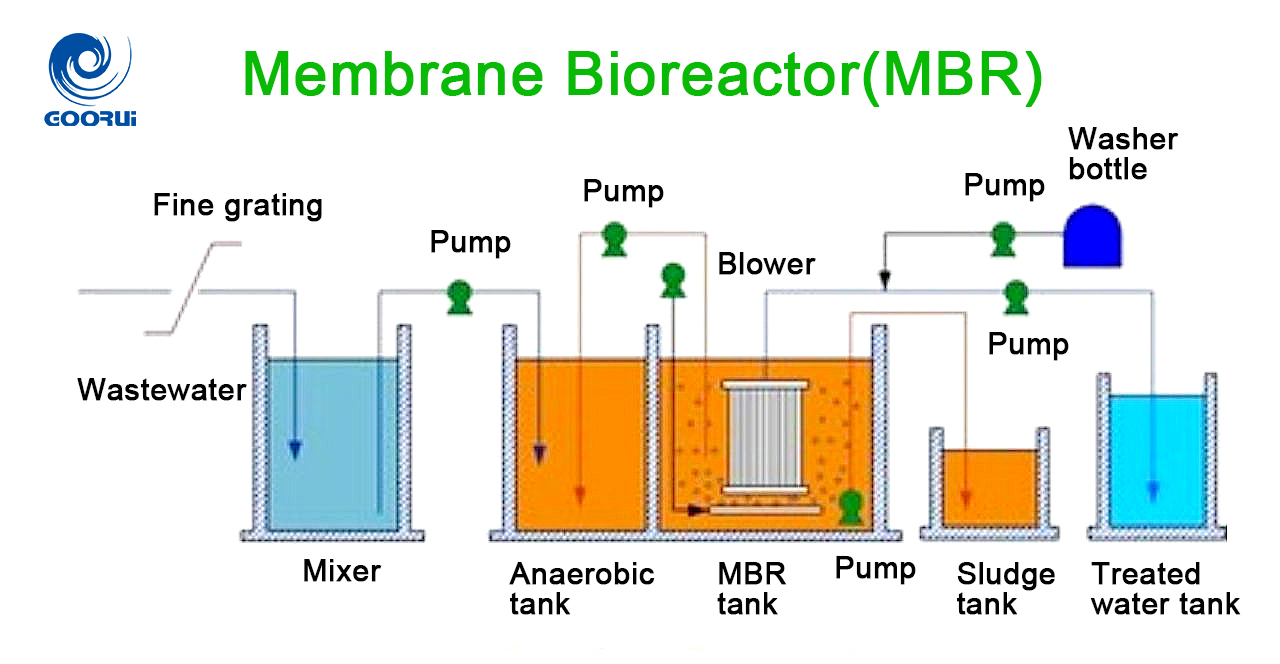
A Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) is an advanced wastewater treatment technology that combines biological treatment (activated sludge process) with membrane filtration.
It’s widely used in sewage treatment plants (STPs) and industrial wastewater treatment because it produces high-quality effluent suitable for reuse.
Key Components of MBR:
Bioreactor (Aeration Tank):
·Works like the activated sludge process where microorganisms break down organic pollutants (BOD, COD).
·Aeration supplies oxygen and keeps biomass in suspension.
Membrane Filtration Unit:
·Microfiltration (MF) or Ultrafiltration (UF) membranes (0.1–0.4 µm pore size).
·Can be configured as submerged (immersed in the aeration tank) or side stream (external module).
·Separates treated water from mixed liquor, eliminating the need for secondary clarifiers.
How MBR Works:
·Raw sewage enters the bioreactor → microorganisms degrade pollutants.
·Mixed liquor is passed through the membranes → solids, bacteria, and pathogens are retained.
·High-quality permeate (treated water) is collected → suitable for reuse (toilets, cooling, irrigation, etc.).
Advantages of MBR:
·Produces very high-quality effluent (low BOD, TSS < 1 mg/L, nearly pathogen-free).
·Compact footprint – no secondary clarifier needed.
·High MLSS (mixed liquor suspended solids) concentration → better treatment efficiency.
·Easier to meet stringent discharge norms or achieve water reuse.
·Modular and scalable design.
Challenges / Disadvantages:
·Higher CAPEX & OPEX than conventional ASP or SBR.
·Membrane fouling & clogging → requires periodic cleaning.
·Energy-intensive (aeration + suction for membrane filtration).
·Skilled operation & maintenance needed.
Applications:
·Municipal wastewater treatment (apartments, hotels, hospitals, smart cities).
·Industrial wastewater (textiles, pharma, food & beverage, chemical).
·Water reuse projects (cooling towers, landscaping, flushing).
In short:
MBR = Activated Sludge Process + Membrane Filtration → gives crystal-clear treated water suitable for reuse.